
- Nodebox linguistics parser how to#
- Nodebox linguistics parser software#
- Nodebox linguistics parser code#
The current version of the parser requires Java 8 or later.
Nodebox linguistics parser how to#
The included usage message gives a detailed description of how to use the tool. This tool measures scores for dependency trees, doing F1 and labeled attachment scoring. The package includes a tool for scoring of generic dependency parses, in a class .DependencyScoring. The models for this parser are included in the general Stanford Parser models package. The parser outputs typed dependency parses for English and Chinese. In version 3.5.0 (October 2014) we released a high-performance dependency parser powered by a neural network.
Nodebox linguistics parser code#
(See also the current Universal Dependencies documentation,Īs of version 3.4 in 2014, the parser includes the code necessary to run a shift reduce parser, a much faster constituent parser with competitive accuracy. This style of output is available only for English and Chinese.įor more details, please refer to the Stanford Dependencies webpage and the The parser provides Universal Dependencies (v1) and Stanford Dependencies output as The parser has also been used for other languages, such as Italian, The Penn Arabic Treebank are also included. Parser based on the Negra corpus and Arabic parsers based on
Nodebox linguistics parser software#
Or the software can be used simply as an accurate unlexicalized stochasticĮither of these yields a good performance statistical parsing system.Ī GUI is provided for viewing the phrase structure tree output of the parser.Īs well as providing an English parser, the parser can beĪnd has been adapted to work with other languages.Ī Chinese parser based on the Chinese Treebank, a German Phrase structure and lexical dependency experts, whose preferencesĪre combined by efficient exact inference, using an A* algorithm. The lexicalized probabilistic parser implements a factored product MacCartney, Anna Rafferty, Spence Green, Huihsin Tseng, Pi-Chuan Chang, Wolfgang Teg Grenager, Galen Andrew, Marie-Catherine de Marneffe, Bill User support, etc.) has been done by Roger Levy, Christopher Manning, Modeling, flexible input/output, grammar compaction, lattice parsing, With support code and linguistic grammar development by Christopher Manning.Įxtensive additional work (internationalization and language-specific The original version of this parser was mainly written by Dan Klein, This package is a Java implementation of probabilistic natural languageīoth highly optimized PCFG and lexicalized dependency parsers, and a Natural language processing in the 1990s. Their development was one of the biggest breakthroughs in These statistical parsers still make some mistakes, but Hand-parsed sentences to try to produce the most likely analysis of new
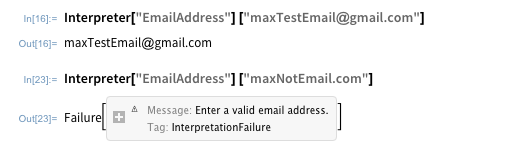
Probabilistic parsers use knowledge of language gained from

(as "phrases") and which words are the subject or object of a Structure of sentences, for instance, which groups of words go together A natural language parser is a program that works out the grammatical


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
